When the summer heat arrives, or when the pressure to maintain comfortable temperatures in large commercial or industrial spaces intensifies, chilled water systems become the unsung heroes. These systems are designed to keep our buildings cool by using water as a heat-absorbing medium, instead of traditional air conditioning. But have you ever wondered how exactly they work? Well, let’s dive into it, and I’ll share all the essential details you need to know.
The Basics of Chilled Water Systems
In simple terms, a chilled water system is a type of cooling system that uses water to absorb and remove heat from spaces, typically commercial buildings or industrial plants. Instead of relying solely on air, it circulates cooled water through pipes, reducing the temperature of air in specific zones. By the end of this process, the water returns to the chiller to be re-cooled, and the cycle repeats. The main goal is to maintain a cool and comfortable environment.
Chilled water systems are incredibly effective for large facilities because they can handle the heat load of multiple rooms or sections within the building. So, whether it’s a factory, a hotel, or an office block, a chilled water system is an efficient and reliable way to maintain the right temperatures year-round.
Here’s How It All Works:
The Chiller: This is the core of the system. It’s responsible for cooling the water by using a refrigeration cycle. The chiller absorbs the heat from the water, which is then transferred to either condenser water or released into the outside air.
Chilled Water Loop: A network of pipes and pumps circulates the chilled water throughout the building, cooling different areas.
Air Handling Units (AHUs) and Fan Coil Units (FCUs): These are crucial in transferring the cold energy from the water to the air. The chilled water is pumped through coils, and then fans blow air across these coils, releasing cool air into the environment.
Heat Absorption: As the chilled water moves through the building, it absorbs heat from the air. The now-warmed water returns to the chiller to be cooled again.
Cooling Tower: In larger systems, cooling towers work to enhance efficiency by helping to remove excess heat from the condenser water loop, ensuring that the system operates at optimal performance.
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s break it down a little further so you can truly grasp how a chilled water system works in your space.

What Are the Types of Chilled Water Systems?
Understanding the different types of chilled water systems is key in selecting the right one for your needs. Here are the main types, categorized by their chillers and compressors:
Types of Chillers:
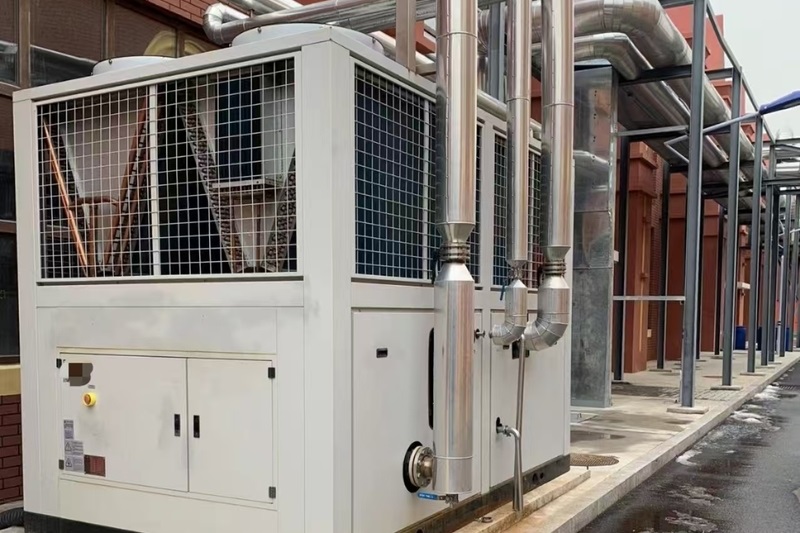
Air-Cooled Chillers: These are typically installed outdoors and expel heat directly into the air through a condenser coil. The refrigerant runs through the coil, shedding heat as the air blows over it. These systems are ideal for smaller installations or places where water resources are limited.
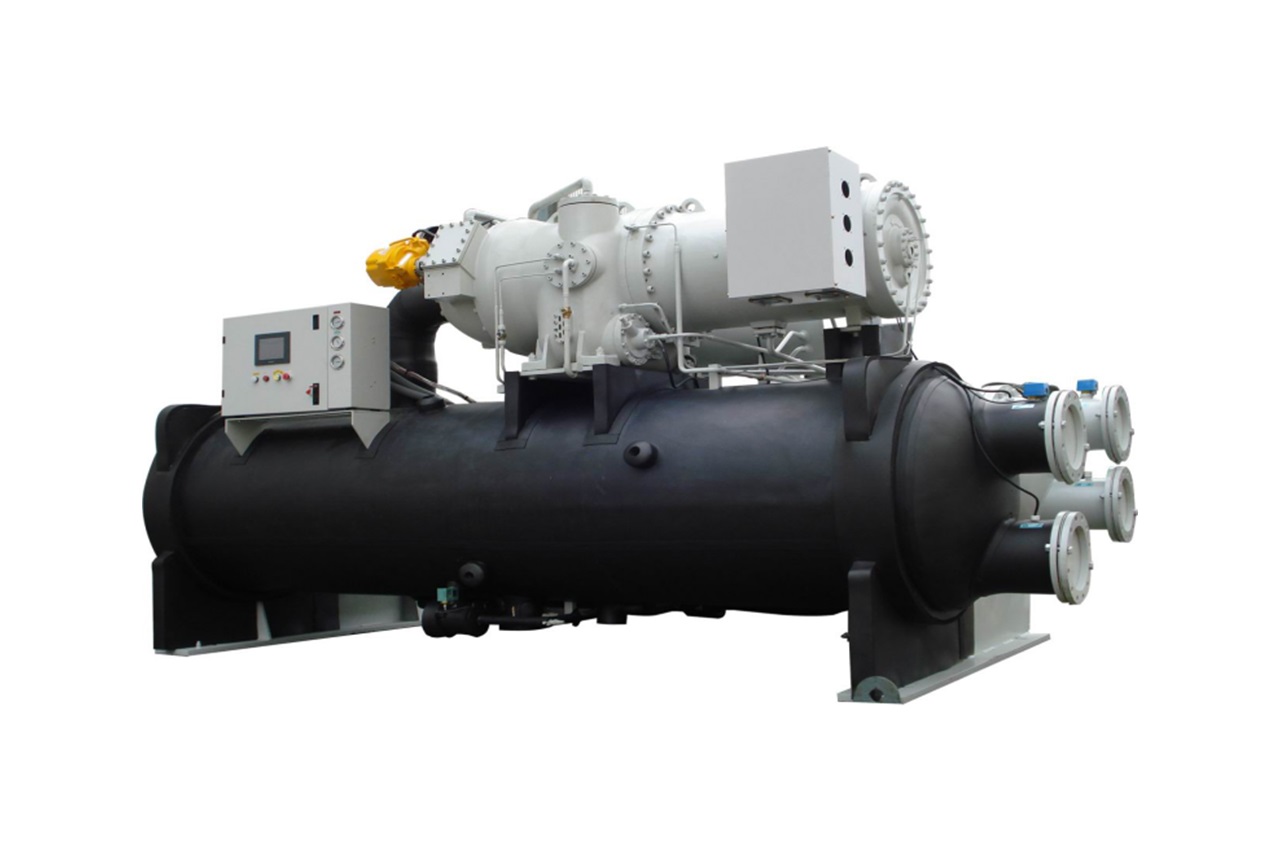
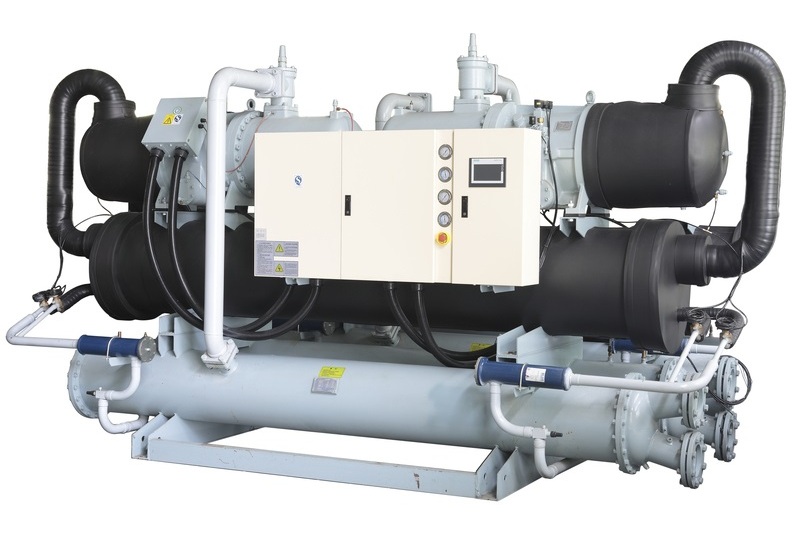
Water-Cooled Chillers: These are more efficient and are typically found inside buildings. They transfer heat from the chilled water to a separate condenser water loop, which is then cooled in a cooling tower. These chillers are often used in larger buildings or industrial setups.
Absorption Chillers: Instead of using electricity, absorption chillers use heat to power the refrigeration process. They rely on heat sources like steam, hot water, or burning oil. These systems are commonly used in industries where there is excess heat available.
Types of Compressors:
Reciprocating Compressors: Used in smaller chiller systems, these compressors are cost-effective but may not be as efficient for larger applications.
Scroll Compressors: These compressors are more efficient than reciprocating types and are widely used in medium-sized chillers.
Helical-Rotary (Screw) Compressors: With fewer moving parts, screw compressors offer better reliability and efficiency compared to reciprocating compressors.
Centrifugal Compressors: These are typically used in large-scale chiller systems due to their high efficiency and reliability.
Each type of chiller and compressor serves a specific function depending on the scale of the operation and the efficiency needs of the space.

Common Problems with Chillers
While chilled water systems are efficient, they do come with potential issues, especially when it comes to maintenance and operation. Understanding the common problems can help ensure you’re able to troubleshoot effectively and maintain peak performance.
Maintenance Issues:
Neglecting Regular Maintenance: Without regular inspection and maintenance, chillers can lose efficiency, leading to increased energy consumption. It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines on routine maintenance.
Infrequent Filter and Lubricant Changes: Filters and lubricants play a key role in ensuring the system runs smoothly. Dirty filters can obstruct airflow, while old lubricants may cause excessive wear on parts.
Condenser Tube Fouling: This occurs in water-cooled systems, where dirt or scale buildup can reduce heat transfer efficiency, leading to system failure.
Operational Issues:
Improper Operation: Poor operation, such as incorrect temperature settings or improper flow rates, can cause a system to underperform. This is why staff training is crucial.
Inadequate Pumping: Low flow rates or pump failure can significantly reduce the efficiency of the entire system, leading to insufficient cooling.
Refrigerant Leaks: Leaks reduce the cooling capacity of the chiller and can cause environmental hazards. Detecting leaks early on is crucial to avoid further damage.
Environmental Issues:
High Discharge Pressure: This often happens when the water treatment process is inefficient, leading to mineral and dirt buildup in the condenser loop.
Unusual Noises: Grinding or rattling noises often indicate issues with the compressor or other moving parts that may need to be repaired.

Conclusion
In conclusion, chilled water systems are a vital part of modern infrastructure, offering an efficient way to cool large spaces and industrial applications. Understanding how these systems work, the types of chillers available, and how to troubleshoot common issues can help you maintain an efficient and reliable cooling process for years to come. Whether you’re working in a factory, office, or hotel, investing in the right chilled water system can help optimize energy use, improve comfort, and lower operating costs. So, the next time you’re considering a chilled water system for your space, remember the essential elements we’ve discussed, and you’ll be well on your way to making an informed decision.
For more insights and expert advice on choosing the right industrial refrigeration system for your business, feel free to reach out to us at IceStar Energy Technology Co., Ltd.!