If you manage large-scale cooling applications, you’ve probably wondered whether centrifugal chillers are the right choice. Cooling large industrial plants or commercial buildings efficiently can be challenging. Choosing an inadequate cooling system can lead to high operational costs, downtime, and ongoing maintenance headaches.
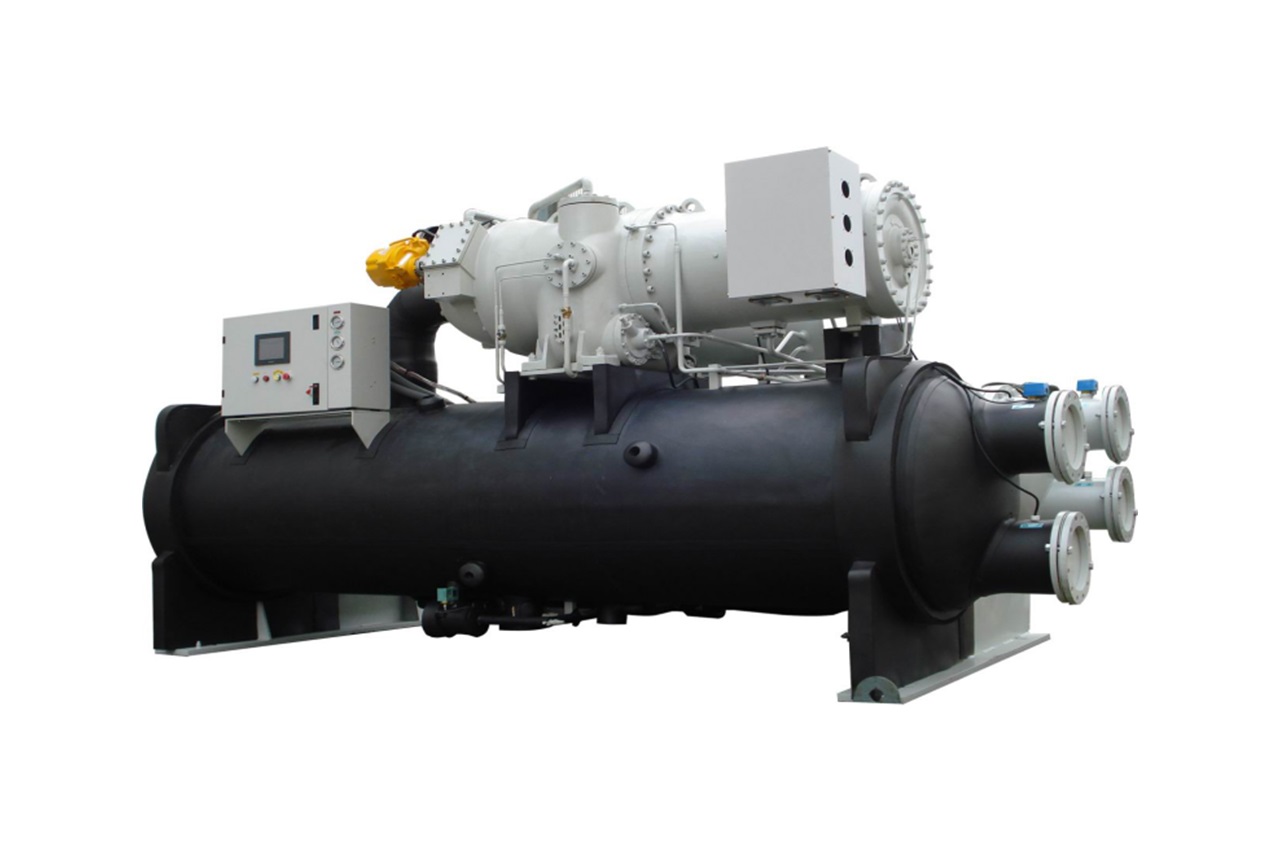
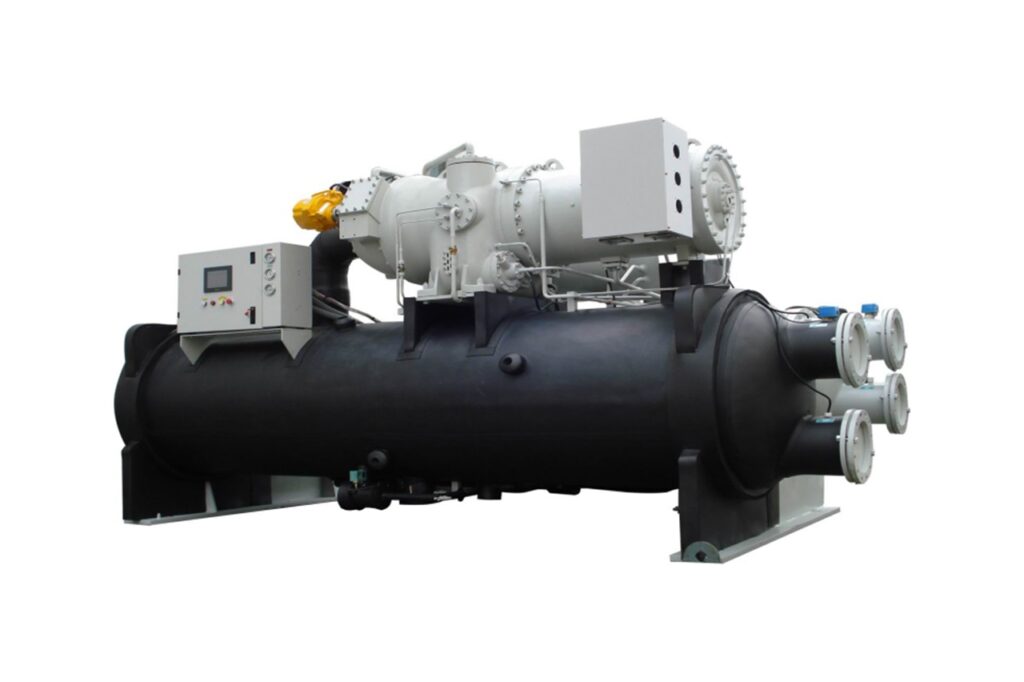
Centrifugal chillers offer exceptional cooling capacity, superior efficiency, compact designs, and long-term reliability, making them ideal for extensive commercial and industrial applications.
So, what exactly makes centrifugal chillers a smart choice? Let’s dive deeper and explore their numerous advantages, real-world applications, and how they compare to other cooling systems.

Why Should You Choose a Centrifugal Chiller?
When you’re responsible for managing cooling systems, you need reliable equipment that delivers consistent performance without inflating your budget. Here’s why centrifugal chillers stand out:
High Efficiency and Cooling Capacity
Centrifugal chillers excel in efficiency and cooling power, often providing capacities from 1,000 to over 10,550 kW. They’re particularly suitable for large-scale cooling needs such as district cooling plants or industrial processes.
- High Efficiency: Many centrifugal chillers achieve Coefficient of Performance (COP) values greater than 6 at full load, significantly reducing energy costs.
- Compact Footprint: They require less space compared to similar-capacity systems, ideal for locations with limited space, such as cruise ships or urban settings.
- Low Maintenance: With fewer moving parts and lubricant-free refrigerants, maintenance requirements and downtime are significantly reduced.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| High Efficiency | COP over 6 at full load; reduces energy expenses |
| Compact Design | Suitable for space-constrained environments |
| Minimal Maintenance | Fewer moving parts; lower maintenance costs |
Flexibility and Environmental Friendliness
Centrifugal chillers also provide exceptional customization and environmental benefits:
- Customization: They can be tailored to specific operational needs, accommodating various refrigerants, including environmentally friendly, low Global Warming Potential (GWP) types such as R-1234ze.
- Cost-Effective: Though initial costs can be higher, the long-term operational savings offset the investment due to their outstanding efficiency.
- Sustainability: Designed to minimize environmental impact by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with global sustainability standards.

Applications Where Centrifugal Chillers Excel
You might be wondering where centrifugal chillers are most commonly utilized.
Centrifugal chillers are most effectively applied in large-scale commercial and industrial environments, including power plants, manufacturing facilities, commercial office buildings, and data centers.
These chillers are perfect where precise temperature control and high cooling loads (typically 150-6,000 tons) are essential. Their consistent and efficient operation helps businesses maintain optimal operational environments, directly impacting productivity and profitability.
- Power Plants: Efficiently manage cooling needs of heavy machinery.
- Factories: Ensure ideal temperature control in manufacturing processes.
- Commercial Buildings: Provide reliable air conditioning for extensive areas.
- Data Centers: Maintain exact temperatures critical for electronic equipment.
- Industrial Processes: Ideal for food processing, metal finishing, and plastic injection molding.

Centrifugal vs. Screw Chillers: Which Is Better?
Making the right choice between a centrifugal chiller and a screw chiller depends on your specific cooling requirements.
Centrifugal chillers are best for extensive applications requiring high cooling capacity and efficiency, whereas screw chillers suit smaller-scale operations needing excellent part-load efficiency and quieter operation.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Aspect | Centrifugal Chiller | Screw Chiller |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Capacity | 1,000-10,550 kW | Smaller to medium capacities |
| Efficiency | High at full load | Good at partial loads |
| Noise Level | Higher | Lower |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Moderately high |
| Best Used For | Large-scale cooling applications | Moderate cooling loads, quiet operation |
For additional insights into the detailed comparison between chiller types, you might find ASHRAE’s HVAC guidelines beneficial.
Absorption Chiller vs. Centrifugal Chiller: What’s the Difference?
Confused between absorption and centrifugal chillers? Here’s clarity:
Absorption chillers use heat sources, often waste heat, making them cost-effective for cogeneration scenarios, whereas centrifugal chillers use electricity, providing higher efficiency and quicker response in large-scale operations.
Key differences include:
| Feature | Absorption Chiller | Centrifugal Chiller |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Waste heat or natural gas | Electricity |
| Efficiency (COP) | 0.7 to 1.4 | Typically 6 to 6.5 |
| Noise & Vibration | Low | Higher |
| Initial Investment | Higher | High, but offset by efficiency gains |
| Ideal Applications | Cogeneration plants, waste heat utilization | Large-scale cooling with rapid load response |
Making the Right Cooling Decision
Choosing the appropriate cooling system isn’t just about upfront costs; it’s about long-term value and efficiency. By understanding these key differences, you can confidently decide which system suits your needs, providing optimal performance and cost savings.
At IceStar Energy Technology, we leverage over 20 years of industry experience to deliver customized industrial refrigeration and heat exchange solutions that perfectly align with your specific requirements.
When you partner with us, you’re not just getting equipment; you’re gaining a reliable, expert-driven solution.
Feel free to contact us to discuss your project today!