As industries continue to grow and evolve, the need for energy-efficient solutions becomes more pressing. Chiller systems, which play a critical role in cooling processes across various sectors, are no exception. Retrofitting your chiller system is a cost-effective way to enhance its performance without the need for a complete replacement. This approach not only extends the lifespan of your equipment but also improves energy efficiency, leading to significant savings on operational costs.
Upgrading your existing chiller system allows you to take advantage of modern technologies, which can optimize performance, reduce energy consumption, and contribute to a more sustainable environment. However, with so many options available, it can be overwhelming to decide where to start.
In this article, I’ll walk you through how chiller systems can be retrofitted to boost performance, including practical tips and insights that will help you make informed decisions for your business. Let’s explore how simple modifications can deliver outstanding results.
Why Retrofit a Chiller System?
You may have noticed rising energy bills, unexpected breakdowns, or performance issues with your existing chiller system. These are common signs that your equipment could benefit from retrofitting. Retrofitting allows you to upgrade key components and systems within your chiller without incurring the high costs associated with a full replacement. It’s a smarter, more affordable way to breathe new life into your system and improve its overall performance.
Chiller retrofitting focuses on improving the efficiency of existing systems by upgrading specific components. These upgrades typically involve replacing or enhancing outdated parts such as compressors, fans, pumps, and control systems. Not only does retrofitting help extend the lifespan of your equipment, but it also ensures that your system runs more efficiently, saving you money in the long term.
For example, retrofitting with energy-efficient components, like compressors and Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs), can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%. This allows you to reduce operational costs while boosting your chiller’s performance. Furthermore, these retrofits often require minimal downtime, so your business won’t experience significant disruptions.

Key Retrofit Strategies for Chiller Systems
Compressor Upgrades
One of the most effective ways to enhance chiller performance is by upgrading the compressor. Replacing outdated compressors with modern, high-efficiency models can significantly reduce energy consumption. Modern compressors, such as scroll or variable-speed compressors, can reduce energy usage by as much as 9% compared to older models. These compressors adjust their speed depending on cooling needs, improving overall efficiency and reducing the load on your system.
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) are a powerful tool for improving chiller system performance. These devices allow the compressor to adjust its speed based on cooling demand. By matching the compressor’s speed to the actual load, VFDs can save up to 20% of energy consumption. This is particularly useful in facilities where cooling needs fluctuate throughout the day, allowing for more efficient operation without overburdening the system.
Chilled Water and Condenser Water Reset
Both chilled water and condenser water reset strategies can help improve chiller efficiency. Raising the chilled water setpoint during partial load conditions allows the compressor to reduce its cooling capacity request, improving performance by 1-2% for each degree Fahrenheit increase. Similarly, lowering the condenser water setpoint during low building load or cooler outdoor temperatures reduces the pressure of condensation, saving 1-2% of energy for every degree Fahrenheit lowered. These simple adjustments can result in substantial energy savings over time.
Heat Exchanger Cleaning and Maintenance
Heat exchangers play a crucial role in maintaining chiller efficiency by transferring heat between fluids. Regular cleaning and maintenance of heat exchangers ensure optimal heat transfer, which is vital for keeping your system running efficiently. Without proper maintenance, heat exchangers can become clogged or fouled, reducing their effectiveness and causing your chiller to work harder, thus consuming more energy.
Pump and Fan VFDs
Just like with compressors, applying VFDs to circulation pumps and air handlers allows you to modulate the flow rates according to need. This enables the system to operate at optimal efficiency, reducing energy consumption by up to 30%. By adjusting pump and fan speeds based on actual cooling requirements, you can further optimize your chiller system’s energy use.
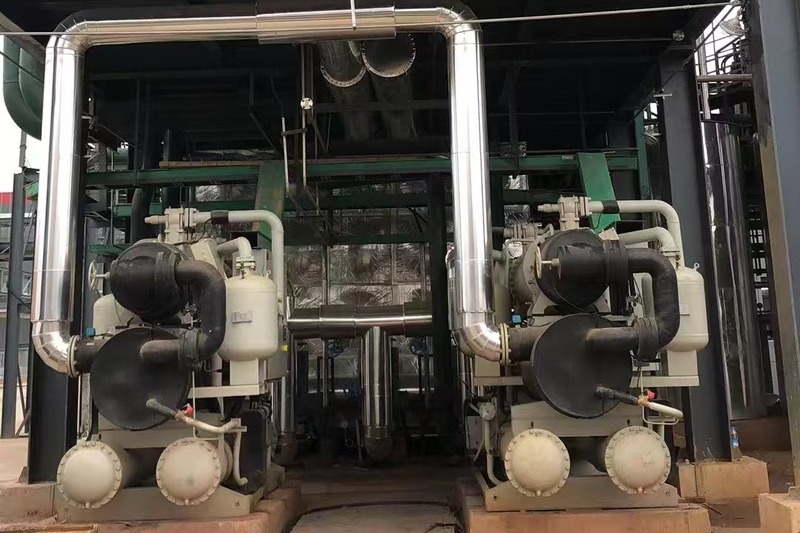

Understanding Chiller Efficiency
Chiller efficiency is an essential factor in determining how well your system is performing. There are several metrics you can use to evaluate a chiller’s efficiency, including the Coefficient of Performance (COP) and the Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER). These measures provide insights into how efficiently your chiller converts energy into cooling.
Coefficient of Performance (COP): This ratio indicates how much cooling a chiller provides for each unit of energy consumed. A higher COP means better efficiency.
Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER): EER compares the chiller’s cooling output to its electrical consumption under specific operating conditions.
kW/ton: This metric tells you how much energy (in kilowatts) is required to produce one ton of cooling. Lower kW/ton values signify better efficiency.
To achieve the best efficiency, consider upgrading your chiller system’s key components to match modern standards. This can reduce energy consumption while maintaining or improving cooling performance.
The Advantages of Water Cooling Over Air Cooling
When choosing between water-cooled and air-cooled chiller systems, water cooling generally offers superior performance. Here’s why water cooling is often considered more effective than air cooling:
Higher Thermal Conductivity: Water is far more efficient at transferring heat than air, allowing water-cooled systems to maintain lower temperatures and perform better over time.
Greater Specific Heat Capacity: Water can absorb more heat without significantly increasing in temperature, making it ideal for high-performance cooling applications.
Effective Heat Dissipation: Water-cooled systems are designed to circulate coolant away from components and through a cooling tower, allowing for more efficient heat dissipation than air-cooled systems.
Reduced Noise: Water-cooled systems operate more quietly since they rely on low-speed pumps rather than high-speed fans, making them ideal for noise-sensitive environments.
Lower Operating Costs: Over time, water-cooled systems generally consume less energy, leading to lower overall operating costs, especially in larger facilities.
While air-cooled systems are simpler and more affordable initially, water-cooled systems are far more efficient in the long run, making them the preferred choice for industrial applications.

Conclusion
Upgrading your chiller system through retrofitting offers a powerful, cost-effective way to enhance performance and energy efficiency. Whether you are replacing compressors, adding VFDs, or upgrading control systems, these improvements can extend the life of your chiller and significantly reduce energy costs. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability and energy efficiency, retrofitting provides a smart solution for businesses looking to optimize their cooling systems without the expense of a full replacement.
By understanding the key retrofit strategies and how they impact your system’s efficiency, you can make informed decisions that benefit both your bottom line and the environment. If you’re looking for a more efficient and sustainable solution for your cooling needs, retrofitting is a step in the right direction. Let’s work together to ensure that your chiller system is operating at its best.